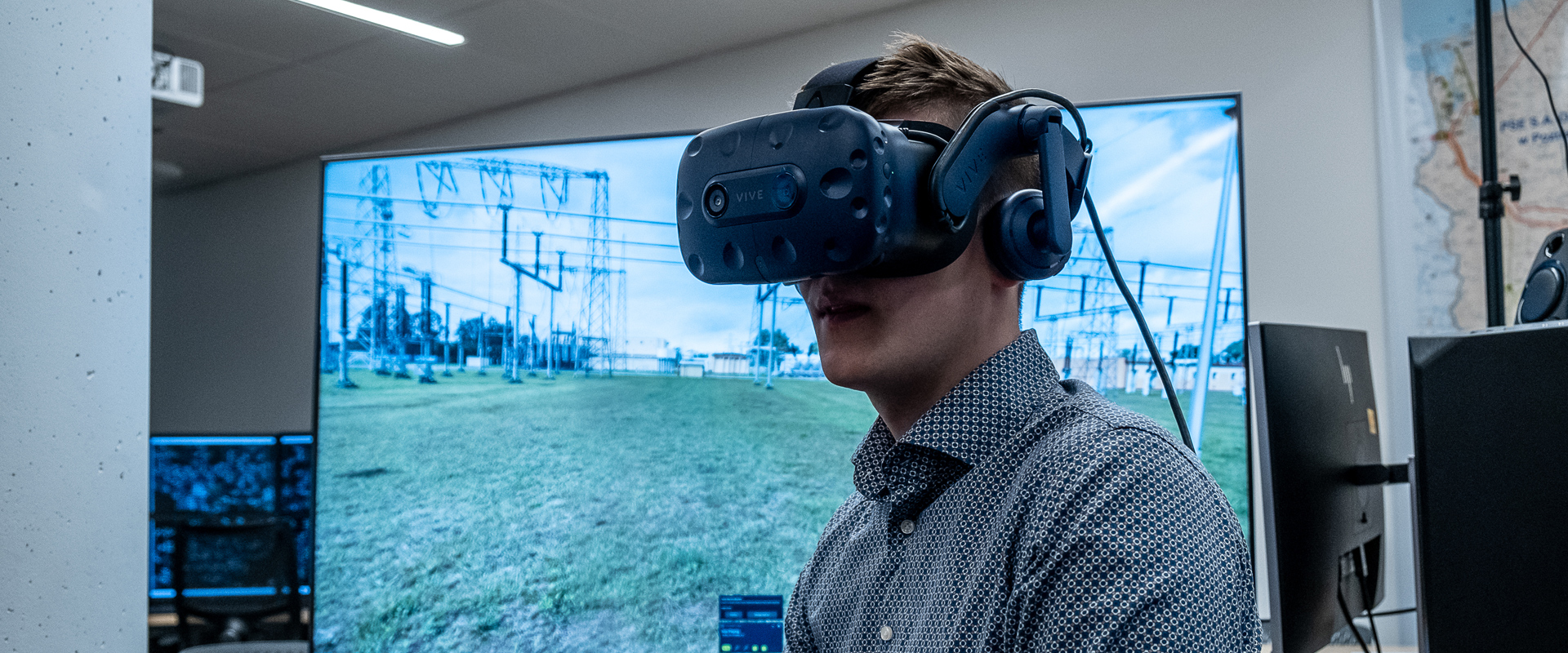

- monitoring of electricity quality of all places of electricity supply to consumers and all substations of the TSO - so that monitoring covers each voltage level in at least one measuring point;
- implementation of the master electricity quality measurement and billing system (SPRJEE), which integrates measurement data from SMJEE systems and is used to process, report and make available JEE indicators and information on JEE parameters to the CSIRE system.
As a result of this task, 2 monitoring systems will be implemented, each covering 130 metering points (260 metering points in total). Upon completion of the task, monitoring of the electricity quality parameters will be carried out at a total of 427 metering points. Additionally, the implemented SMJEE systems will meet very high IT security standards and will implement a number of additional functionalities in line with the standards applicable at TSO. As part of the task implementation, in 2020 the documentation was prepared and agreed upon, and a tender procedure was announced, and in 2021 agreements with contractors were signed and implementation of works planned for the next 3 years began.
The SPRJEE system will make it possible to identify predominant sources of disturbance, determine the parties' contribution to their introduction, and determine discounts, and in the future - if regulated by law - also penalties for exceeding the level of permissible individual parameters. Implementation of the works associated with this task will begin after the IT portion of the SMJEE system is implemented as part of the SMJEE expansion.
- SMJEE - performing data reading from the metering devices installed in the transmission network facilities and serving for their verification,
- SPRJEE - performing the integration of data from the SMJEE systems and responsible for processing, reporting, and sharing JEE indicators and JEE parameter information with the CSIRE system.
- verification of compliance of power quality parameters with the requirements of the system regulation and other applicable regulations at all facilities,
- verification of relevance of applications, claims and notifications of end users, DSO and other NPS users concerning non-compliance with electricity quality parameters, including those related to discounts and network events,
- identification and prevention of new sources of disturbances within the completed connections of RES generators and customers to the transmission grid,
- issuing opinions on wind farm impact test reports on the power system in terms of electricity quality parameters,
- identification of causes of disturbances for electricity quality parameters and identification of the entity responsible for their introduction,
- using the collected measurement data to determine corrective measures and eliminate identified disturbances,
- collecting information on the electricity quality status to determine appropriate requirements for future connections,
- provision of data and recorded events for the evaluation of operation of the equipment in substations and switching operations within the scope of the work of the Commission for Investigation of Disturbances and evaluation of their impact on the plants of entities connected to the transmission system,
- evaluation of applied control automation systems operation - analysis of problems concerning the maintenance of voltage levels and voltage imbalance in the power system.
The measures taken are a response to the growing threats in the cybersecurity sphere. This approach is becoming increasingly important in light of the growing use of new technologies and communication methods. Recent years have seen an increase in threats accompanying new solutions and an increase in targeted attacks using dedicated tools to carry them out, especially on critical infrastructure. Phishing attacks are also becoming more frequent and sophisticated in response to growing user awareness, and ransomware attacks (aimed at extorting a ransom under threat or after making ICT systems or the data itself unusable). The increase in attacks is also related to the current pandemic situation, and the associated increased digitization of life opens up new opportunities to exploit weak points in new solutions and reduced user vigilance.
We have identified possible directions of the situation development, the growing number of cyberthreats and specialized tools for attacking have confirmed the correctness of the assumptions made and the need to continue efforts in this area.
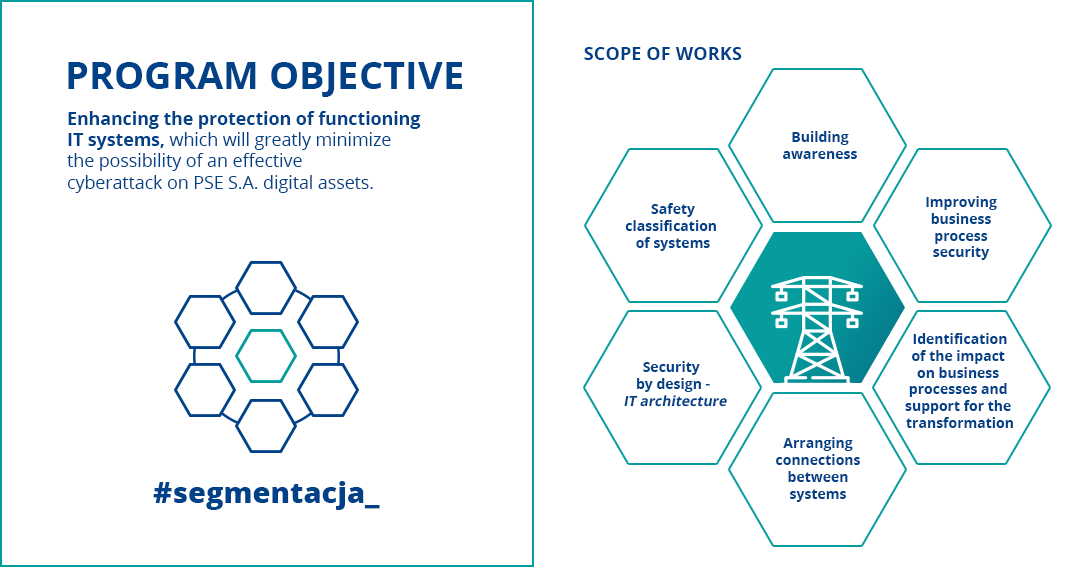
- Network segmentation – projects aimed at ensuring adequate separation of resources with different levels of vulnerability, including ICT systems at the substations and central critical systems - both through actions at the level of technological standards (e.g. EAZ, SSiN), ICT architecture, high-level technical projects for rebuilding ICT network segmentation and appropriate shaping of business projects, and at the level of infrastructure itself;
- Workstation – projects that provide secure work tools to maintain performance and functionality according to business needs, with malware protection and control of permissions and data flow;
- Internet interface – a solution providing our employees and guests with functional and unified access to the Internet (including through a secure WiFi network, implemented both in the company's headquarters and in remote organizational units), taking into account the principles of separation and permission management as well as adequate and secure remote access.
- Detection and Response – To ensure ongoing IT security, a dedicated Security Operations Center (SOC) team performs 7/24 threat monitoring, taking applicable actions and countermeasures for both IT and OT network incidents. Another support line is the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT), which was established in 2016, obtaining relevant certifications in subsequent years, thereby confirming that it meets the highest standards of operation. An important element of this direction is raising employees' awareness, publishing alerts and warnings about threats, reporting information about incidents and cooperation with external entities in the area of ICT security (including CERT NASK, CERT.GOV.PL, RCB).
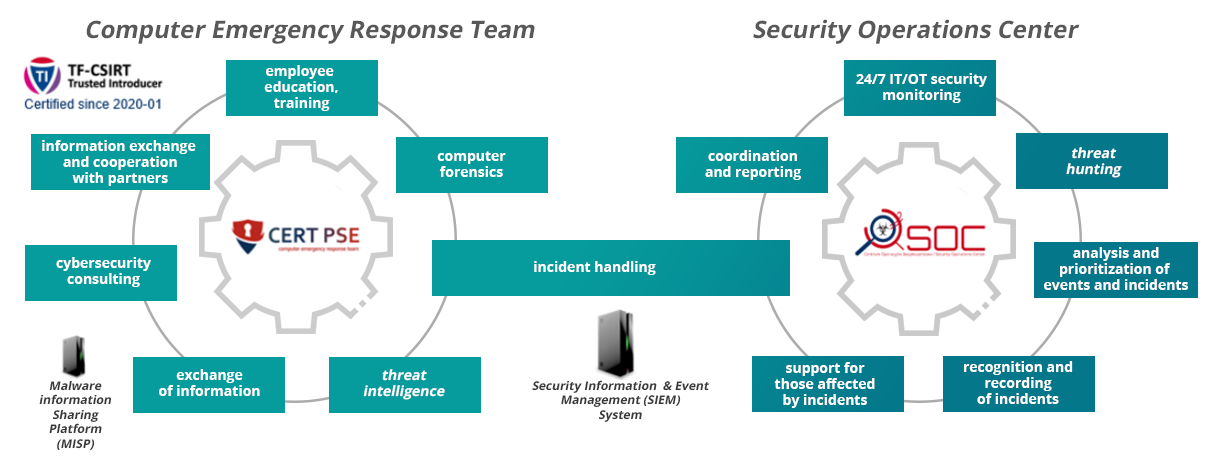
An important activity of CERT PSE is cooperation with the Ministry of Climate and Environment to run the CyberSecurity Team (ZCMK), which was created for the pandemic time. Its idea is to effectively support the crisis management system for organizations in the power sector in the field of CyberSecurity.
- Digital committee Cyber Security Task Force – the team responsible for ENTSO-E's cybersecurity strategy, led by the Director of PSE's ICT Department;
- ENTSO-E Cyber Security Working Group – a group that deals with ICT security issues. Its task is to monitor information about threats in the world and to cooperate in projects where it is necessary to take care of safety and shape rules for safe operation of systems and operators;
- Network Code for Cyber Security Regulation Development Working Group;
- ENTSO-E Working Group EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) – a group that has developed standards for electronic information exchange in the European electricity market.

- Construction of the Żydowo Kierzkowo - Słupsk 400 kV line,
- Construction of the Jasiniec - Grudziądz Węgrowo 400 kV line,
- Construction of a 400 kV line along with the change in the LV network system between Warsaw agglomeration and Siedlce (between cuts of the Stanisławów - Narew line, the Stanisławów - Siedlce Ujrzanów line, the Kozienice - Siedlce Ujrzanów line) - the line was commissioned (the conflict still needs to be altered),
- Construction of the Gdańsk Przyjaźń - Żydowo Kierzkowo 400 kV line with one circuit introduced to the Gdańsk substation (at voltage of 220 kV),
- Construction of the Mikułowa - Czarna 400 kV line,
- Modernization of the Kozienice - Rożki 220 kV line,
- Modernization of the Krajnik - Vierraden 400 kV line in order to adjust it to increased power transmission,
- Extension of the 400/220/110 kV Mikułowa substation for connection of the power unit No. 11 at the Turów Power Plant,
- Extension of the 220/110 kV Jasiniec substation with a 400 kV switching station,
- Extension and modernization of the 400/220 kV Krajnik substation,
- Extension of the 220 kV switching station at the 220/110 kV Piaseczno substation,
- Extension of of the 400/220/110 kV Wielopole substation for connection of 400/110 kV auto-transformer,
- Extension of the 110 kV switching station at the 400/110 kV Mościska substation for connection of 110 kV line of PGE Dystrybucja SA.
On the domestic front, the implementation of Stage I of the balancing market reform coincided with the full launch of the capacity market. This required adaptation of the processes of coordination planning and operation of the national power system and the information systems supporting their implementation. The implementation of the new coordination planning processes required by the capacity market and the balancing market has been carried out together with the implementation of new data exchange rules in accordance with Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1485 of August 2, 2017 laying down guidelines for the operation of the electricity transmission system, which in terms of exchange of structural and planning data imposes new obligations on TSOs, electricity distribution system operators and significant network users.
Along with changes to operational processes and supporting IT systems, security requirements were implemented for newly built systems to reduce the possibility of a successful cyberattack on PSE's digital assets. This work included: division of IT architecture into security zones to ensure adequate security level of particular systems and applications used for accomplishing the tasks of TSO and creation of new runtime environments to build and test IT tools for TSO.
In addition to the implementation of Stage I of the balancing market reform and the full launch of the PSE capacity market, a number of European projects were implemented, including those resulting from the implementation of Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/1222 of 24 July 2015 laying down guidelines for capacity allocation and congestion management, Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/2195 of 23 November 2017 laying down balancing guidelines, and the implementation of the market coupling mechanism in the day-ahead market for the synchronous boundaries of the Polish market area. In 2020, the business capabilities in this area were achieved in: (i) handling of explicit allocation in the intra-day market at the Slovak border, (ii) LFC regulation in compliance with the Imbalance Netting rules (connection of NPS to the IGCC platform), (iii) publication of data on the ENTSO-E information platform using international EIC codes, and (iv) readiness to handle metering and settlement data for the purpose of interconnection exchange with a 15-minute resolution. As a result of intensive works in 2020, the functionality to support multiple NEMOs in the Polish market area (Multi-NEMO Arrangement - MNA) was launched on February 9, 2021.
Parallel to the implementation works carried out in 2020, pre-implementation works were carried out related to the launch of two projects of capital importance for the processes related to managing the operation of the NPS. The first one, scheduled to go live in the second half of 2021, is the purchase and commissioning of a new SCADA/EMS (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition/Energy Management System). The objective of the project is to equip the dispatching services of PSE with IT tools enabling effective performance of tasks in the area of NPS operation, including monitoring of the system operation status, identification of threats to the operation of the NPS system, remote control of network facilities, exchange of real-time data with other transmission and distribution system operators. The system will be equipped with advanced EMS computational tools, performing tasks related to the execution of NPS safety analyses in real time and in the study mode on the basis of telemetric measurements derived from the SCADA subsystem.
The realization of the above, as indicated by examples of implementations at operators in the USA and Europe which are facing similar challenges, is possible through the use of NMMS.
On the basis of this system, adequate business processes related to structural data management will be defined and implemented according to SO GL requirements. This will achieve a coordination planning business capability based on a unified, centrally managed network model that is compliant with the CIM standard. Activities in this area are also necessary due to PSE's participation in the processes of Regional Security Center/Regional Coordination Center.
The purpose of the aforementioned regulations is to implement measures aimed at preventing electricity crises, preparing for them and managing them in a transparent manner and with full regard to the requirements of a competitive European electricity market.
- a significant electricity shortage identified by Member States and described in their emergency preparedness plans
or - inability to supply electricity to customers.
Following the definition by ENTSO-E of 31 regional power crisis scenarios the company evaluated the probability of their occurrence and the impact of their materialization in Poland. A summary of the assessment was provided to ENTSO-E.
PSE, in collaboration with the Ministry of Climate and Environment, participated in defining national scenarios for the electricity crisis. Out of 31 RKEE scenarios, 28 were found to be adequate and relevant to Polish conditions.
PSE is also involved in the work, carried out by the Ministry of Economy, to develop a national emergency preparedness plan for the electricity sector (its preparation is an obligation under Regulation 2019/941).
The extent of required investment in transmission infrastructure depends on a number of external factors, such as demand, supply, and economic and socio-political conditions, among others. Some of these factors are by their nature random. In the current realities of power system operation, there is an increasing demand to incorporate a probabilistic element in the grid development planning process that will allow a more accurate representation of the environment than with the deterministic approach used to date.
On the one hand, probability analyses better reflect reality, but on the other hand, they are characterized by a higher degree of complexity and time-consuming calculations. With this in mind, PSE recognized the need to develop a dedicated tool that would incorporate probabilistic elements into the transmission development planning process while doing so in an efficient manner. As a result of identifying the above mentioned need, a functional concept was developed, and then an IT tool called aPRSP was created. This tool is primarily designed to assist planners in selecting the most cost-effective schedule for implementing network investments while taking into account random factors affecting power system operations.
The aPRSP tool works in two stages. The first stage is the automatic identification of candidates (potential investments consisting of the construction of new or the modernization of existing network infrastructure elements), during which the potential market profits resulting from the construction of a new network element and the capital expenditures to be incurred are compared in a simplified manner. This stage analyzes a virtually unlimited number of candidates but allows the most promising solutions to be quickly identified for more detailed analysis. In the second stage, the narrowed candidate list forms the basis of the actual optimization process. The process is intended to determine the time and task schedule for the implementation of investment activities that minimize the total investment costs and the costs of market operations, while ensuring that the criteria for the safety of system operation are met.
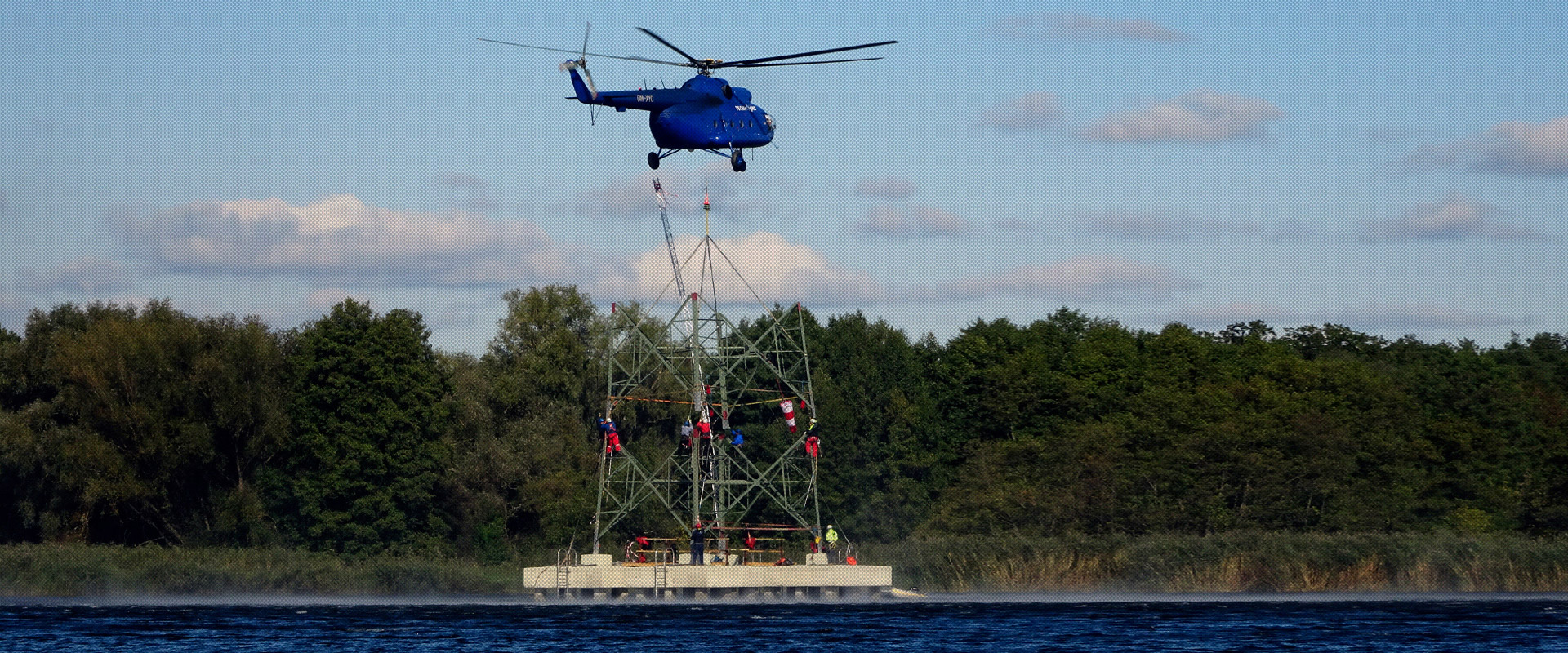

We have started activities to prepare for the current situation already in October 2019. PSE formed an organizational unit in the Department of Security called the Aerial Operations Support Division to prepare for and implement self-performed aerial operations. We purchased 3 new Robinson R66 helicopters, the parameters of which perfectly match the needs of our company, and additionally met the conditions for low purchase and operating costs. The preparatory work was completed at the beginning of 2021, and since February 5, 2021, we have been given the permit PL.SPO.058-HR by the President of the Civil Aviation Authority to carry out commercial high-risk specialized operations. This permit allows to patrol substations, power poles and lines, gas pipelines, other pipelines, and to fly for site inspection and strategic security patrol of the power infrastructure. We employ trained, experienced pilots and task specialists. Helicopters and crews are based in 3 locations around the country, allowing for quick access to all of the power lines. The aerial operations we have carried out have confirmed the high efficiency and speed of transmission infrastructure inspections.
Increasing the number of aircrafts and purchasing helicopters with more favorable maneuvering parameters will allow to: execute more complex aerial operations, use specialized on-board monitoring and reconnaissance equipment, expand tasks in the sphere of security performed in the situation of transmission line failures and unauthorized violation of power substation borders. The increased number of helicopters will enable an increase in the scope of tasks to include, among other things, inspection of the condition of investments and analysis of the terrain during the design and delineation of new lines. Increasing our aerial equipment resources will result in faster arrival of our specialists to failure/outage sites and enable faster response to the incident, thus reducing the time of power outage.
The concept of the transmission network operation assumes, among others, the establishment of the OWF/HVDC Division and defines the scope of the main tasks for this team. In order to provide the employees of the new Department with the necessary conditions and tools to perform their tasks, the company started reviewing office suits in the Trójmiasto area in order to select several preliminary locations. The team carrying out this task visited and reviewed the office suits. Technical analyses were also conducted dedicated to verifying the degree to which the selected office suits meet PSE standards. The next step will be to gather lease or sale offers on the selected office suits and analyze the cost of retrofitting and arranging to meet PSE standards.
All these activities are aimed at ensuring the possibility of operating the transmission network in the area of northern Poland (the area of ZKO Bydgoszcz) after the extension of the transmission network for the connection of offshore wind farms (OWF) and HVDC Harmony Link. The initiative to create and develop our own engineering and technical services, especially in the execution of the most complex tasks - installation and commissioning of secondary circuits of power substations and HVDC technology facilities - will allow us in the future to effectively manage the operation of facilities and incidents, i.e. efficiently remove faults and failures.
To this end, the company is continuing the project to build and implement CSIRE - a centralized system for obtaining, collecting, processing and sharing electricity market information (including metering data), and is preparing to establish OIRE. Under the provisions of the Energy Law, CSIRE is expected to be launched in mid-2024. PSE - acting then as OIRE - will be responsible for managing CSIRE, including in particular for maintaining, operating and developing the information system.
As part of the OIRE Project, at the end of 2020 PSE announced a public procedure in the mode of negotiations with notice for the development, implementation and deployment of a central electricity market information system with supporting services. An ongoing procedure will result in the selection of a contractor for the system.
In Q4 2020 and Q2 2021, we published draft Central Energy Market Information System (SWI) Information Exchange Standards on the PSE website. Ultimately, the proposed document will define, among other things, how retail electricity market processes are to be conducted, communication rules, and the scope of information exchanged between individual market participants via CSIRE. It will also describe the model of roles and market participants and identify recommended scenarios for using the processes to achieve the goals of energy market actors, particularly electricity consumers. The Energy Market Information Exchange Standards will be approved by the President of the Energy Regulatory Office as part of the Transmission Network Code.
Works on the draft SWI have been carried out with respect to the opinions expressed by market participants, with whom PSE continues to cooperate within the Team working under the Minister of Climate and Environment, as well as in working groups established by PSE. The main addressees of the SWI are entities operating professionally in the retail electricity market. Implementation of the document will provide professional users - e.g. distribution system operators (DSOs) and energy sellers (ES’s) - with the possibility of communicating using standardized messages and executing business processes in a standardized manner.
The implementation of the OIRE project aims to achieve the objectives of the retail market stakeholders and the obligations indicated in the legislation, in particular to ensure an effective and secure exchange of information in the area of the retail electricity market, covering the acquisition, storage and sharing of energy market information (including metering data). The operation of OIRE and the functioning of CSIRE will support the implementation of statutory rights and obligations of individual entities operating in the retail electricity market. CSIRE will process, among other things, information on contracts functioning in the retail market and metering data from electricity meters. The processed information will be used to carry out processes such as changing the seller of electricity and making settlements for its sale and supply. With the launch of the system, energy market processes, including the switching of electricity sellers, will be simplified and their implementation time will be shortened.
- Benefits to end users, including prosumers:
- free access to their data (including metering data) related to the energy delivery points where they use electricity,
- make it easier and more efficient to achieve electricity consumption goals, including switching energy retailers,
- the ability to verify individual consumption data and electricity input to the grid,
- the ability to obtain detailed, reliable and user-friendly information to support decision-making as regards the use of electricity, optimizing consumption and reducing the cost of electricity use,
- the ability to make own energy market information, including metering data, available to selected entities, e.g. in order to receive more favorable, individually tailored commercial offers, including those concerning additional services,
- ensure information security and personal data protection in accordance with requirements of the European Union.
- Benefits to electricity market participants:
- reducing the cost of operation for entities in the retail electricity market and lowering the barrier to entry by reducing the number of interfaces and creating a single point of access to energy market information,
- the ability to exercise statutory rights and obligations through the efficient and secure exchange of information in the retail energy market through CSIRE,
- unification of rules for execution of retail electricity market processes within the framework of legally defined division of roles and responsibilities,
- guarantee of data processing efficiency and sustainability in the CSIRE solution,
- enabling the creation and development of new services by facilitating access to energy market information, including metering profiles for electricity consumption and generation,
- transparency of retail energy market processes supported by CSIRE,
- the possibility of obtaining energy market information on potential customers (only upon the customer's consent), e.g. for the purpose of preparing personalized offers.
- Benefits to the national power system and power system operators:
- improving the efficiency of NPS resources use, among others through better matching of energy consumption to its generation, in particular from RES,
- the ability to perform integration of retail and system market processes using metering data available in CSIRE,
- improvement of metering data quality through the use of uniform standards and quality benchmarks,
- the ability to use a uniform standard of aggregated metering data to meet statutory obligations.
At the same time, in order to protect customers from excessive or abrupt increases in fee rates, work is underway to implement a cost adjustment account mechanism.
Supplement - PSE's strategy (2-year horizon)
of the teams
business continuity
in demand
generation adequacy
of the electricity market
Export
Goals:
Maintaining business continuity is critical to the tasks performed by the power transmission system operator. Securing full availability of critical area staff: National Dispatch Center (KDM), Area Dispatch Center (ODM), network operations, data communications, or security during an epidemic emergency or possible quarantine.
- Retraining some of the available workforce
- Attracting and recruiting new people
Goal:
Maintaining the redundancy of the National Power System (NPS) facilities, first of all the centers for: dispatching (KDM and ODM), supervision (CN and RCN), operations (NOC and SOC) and rooms dedicated to office work (also such where it is possible to carry out critical processes, e.g. managing servers or market and dispatching applications), as well as the redundancy of message transfer routes (remote substation control, WAN nodes, etc.).
- Provision of facility redundancy
Goals:
An undeniable consequence of the business activity decline is a reduction in electricity demand. The result may include:
1. a downturn in the energy market causing a weakening of investment signals and, as a result, a progressive erosion of the generation base,
2. reduction of the electricity price carrier for PSE's revenue calculation and, as a result, the stranding of part of the company's costs (primarily fixed costs),
3. problems with voltage regulation (reactive power distribution) related to the lack of load for the extra high voltage lines and substation switchgears.
- Reducing operating costs
- New system services
Goal:
The capacity market mechanism currently provides financing for generating units. The loss of financial support for coal-fired generating units from 2026 is a threat (as per CEP70). This risk, together with the abandonment of ongoing maintenance, withholding of retrofits and new investments due to the development of the pandemic, could result in a loss of generation adequacy and, consequently, problems with balancing the national power system. It is therefore critical to identify and implement countermeasures to mitigate the risk of loss of generation resources.
- Developing a methodology for assessing the risk of maintaining electricity generation sufficiency
Goal:
The economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and the accompanying decline in demand for electricity may account for declines in energy prices in both the balancing market and the Polish Power Exchange.
- Playing for Time (ongoing analysis of the financial condition of energy market participants)
Goal:
The expected effect of implementing prevention activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic may be to exacerbate conflicting trends:
- protectionist trends - strongly reducing energy imports (both in Poland and in neighboring countries),
- opportunistic trends - increased trading of electricity between interconnected systems due to unpredictable and high price differences between national energy markets.
- Maintaining the continuity of the investment process
As part of the cooperation with DSOs and public administration, principles were developed for the functioning of the mechanism of the so-called adjustment account, covering adjusted revenues of companies providing electricity transmission and distribution services. It consists in recovering in subsequent years the uncollected revenues or giving back the surplus of revenues obtained from the application of tariff rates in relation to the planned values, while maintaining the specified maximum level of variability of tariff rates in subsequent years.
The Company actively participated in the legislative process of agreeing on the mechanism and subsequent implementation of the agreed adjustment account model into regulations. The agreed provisions regarding the revenue adjustment account have been included in the Regulation of the Minister of Climate and Environment of November 13, 2020 amending the Regulation on the detailed rules for shaping and calculating tariffs and settlements in electricity trade.
In 2020, PSE also developed a concept for a model of the so-called cost adjustment account, which was submitted for consultation to the Energy Regulatory Office.
In 2020, the implementation concept for flexibility services and frequency-independent services provided by system users was developed, as well as proposals for appropriate provisions of legal regulations implementing the provisions of Directive 2019/944. The work took place with the participation of representatives of the Ministry of Climate and Environment, the Energy Regulatory Office and distribution system operators. In 2021, comments were prepared on the proposal to implement Directive 2019/944 (draft amendment to Law No. UC74) proposed by the Ministry of Climate and Environment.
At the same time, as part of the implementation of works related to broadly defined flexibility services, PSE joined the OneNet international research and development project, which received EU funding. The objective of the project is to formulate the execution concept for the project works and its implementation, with particular focus on the Polish demonstrator, i.e. to define, test and demonstrate the procurement of services from flexibility sources that can be used in the future to support network management by system operators. The OneNet project began on October 1, 2020 and will run through September 30, 2023. The products which PSE is interested in purchasing on a test basis from entities connected to the MV and LV distribution network have been identified.
- addressing regulatory requirements (including CEPs and network codes),
- necessary for effective connection of new entities,
- supporting the transformation of the national electric power industry,
- providing remote control of NPS devices.

Methodology for determining VOLL, CONE and RS
- VOLL (Value of Lost Load) – which determines the cost of a new unit going into effect. This index measures the alternative cost of acquiring capacity by building the generating unit with the lowest operating and capital fixed costs.
- CONE (Cost of New Entry) – określającego koszt wejścia w życie nowej jednostki. Wskaźnik ten określa alternatywny koszt pozyskania mocy poprzez budowę jednostki wytwórczej o najniższych operacyjnych i kapitałowych kosztach stałych.
- RS (Reliability Standard) – which defines the level of safety standard in the power system. The safety standard under the methodology is fundamentally determined as the ratio of the cost of entering a new unit to the designated value of energy not served. The standard is set in the form of the LOLE index.
- the expected amount of energy not served (Expected Energy Not Served – EENS),
- the expected time of power outage (Loss of Load Expectation – LOLE).
Methodologies for foreign capacity participation in capacity mechanisms
- determining the maximum generating capacity that can be used for the participation of foreign units in capacity mechanisms;
- revenue sharing from capacity allocation;
- rules for conducting availability checks on foreign capacity suppliers;
- the terms and conditions for charging an unavailability fee;
- rules for maintaining the European register of capacity suppliers;
- rules for identifying units eligible to participate in the various capacity mechanisms.
The primary task faced by ORUiM is to keep the stocks at an appropriate level. The standard specifies the minimum number of devices of each type that must be kept on the storage reserve in order to ensure the continuity of the company's operations (e.g. in an emergency situation). For this purpose, ORUiM periodically concludes and executes contracts for the supply of equipment and materials - one-off and framework purchase contracts, concluded for a period of 3 years.
At the end of 2020, the stock stored on the Department of Operations' storage reserve consisted of 4,967 material indexes.
| Number of material indexes of key equipment types at the end of 2020 | |
|---|---|
| Type of equipment and materials | Quantity on reserve |
| Circuit breakers | 55 |
| Measuring transformers | 713 |
| Isolating switches | 185 |
| Surge arresters | 141 |
| Poles | 63 |
The benefits of the above work include, among others, support for shaping the work organization and hiring plan in a way that ensures operation continuity of key teams, taking into account random events beyond the company's control and their possible impact on the availability of key team staffing.
